TensorFlowで学習を行っていると, 学習の収束状況を確認するために, lossやaccuracyが学習とともにどのように変化していくか, 視覚化したくなることがある.
そこで, 今回はスカラ値を視覚化する方法についてまとめておく.
基本的な流れ[1]
ⅰ) SummaryWriterのインスタンス取得
writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter(logdir, graph_def)
ⅱ) 出力したいスカラ値の指定
tf.scalar_summary(name, loss)
ⅲ) すべてのSummaryを結合
merged = tf.merge_all_summaries()
ⅳ) Summaryの評価
summary_str = sess.run(merged)
ⅴ) 評価結果をSummaryWriterに渡す
writer.add_summery(summary_str, step)
Deep MNIST for Expertsを例に, サンプルコードを載せておく.
[コード]
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import os import sys import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf # MNISTデータセットの読み込み from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True) class Option: def __init__(self): self.mode = 'LT' self.model = ''; # 引数チェック def options(argv): opt = Option() i = 0 while i < len(argv): if argv[i] == '-mdl': opt.model = argv[i+1] i+=2 elif argv[i] == '-mode': if argv[i+1] == 'T' or argv[i+1] == 'L' or argv[i+1] == 'LT': opt.mode = argv[i+1] i+=2 else: return False, opt else: return False, opt return True, opt # 重み & バイアス初期化 def weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) return tf.Variable(initial) # 畳み込み & プーリング def conv2d(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='SAME') def max_pool_2x2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1,2,2,1], strides=[1,2,2,1], padding='SAME') def main(opt): # 特徴ベクトルx[][784] ← 784次元(28x28dot) x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 784]) # 目標 y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 10]) # 4次元tensorに変換 x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1,28,28,1]) # 1層畳み込み層 W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,1,32]) b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1) h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) # 2層畳み込み層 W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,32,64]) b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2) h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) # 密に結合された層 W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64, 1024]) b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64]) h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) # ドロップアウト keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) # 読み出し層 W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10]) b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2) cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv)) ce_summary = tf.scalar_summary('cross_entropy', cross_entropy) train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) acc_summary = tf.scalar_summary('accuracy', accuracy) # Saver saver = tf.train.Saver() # セッション sess = tf.Session() # ログ出力準備 merged = tf.merge_all_summaries() summ_writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter('./log/mnist', sess.graph) # 初期化 sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 学習パラメータの復元 if opt.model != '': if opt.model == 'auto': if tf.train.get_checkpoint_state('./'): ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state('./') last_model = ckpt.model_checkpoint_path saver.restore(sess, last_model) elif os.path.isfile(opt.model): saver.restore(sess, opt.model) if opt.mode == 'L' or opt.mode == 'LT' or opt.model == '': for i in range(20000): # ミニバッチのデータ 50個 batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50) # small batch if i%100 == 0: summary, train_acc = sess.run([merged, accuracy], feed_dict={ x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0}) summ_writer.add_summary(summary, i) print "step %d, training accuracy %g"%(i, train_acc) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5}) # 途中の学習パラメータ保存 if (i + 1) % 100 == 0 and opt.model != '': saver.save(sess, opt.model, global_step=i+1) # 評価 if opt.mode == 'T' or opt.mode == 'LT': acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1.0}) print 'test accuracy %g'% acc # セッションクローズ sess.close() if __name__ == '__main__': ret, opt = options(sys.argv[1:]) if ret == False: sys.exit("Usage: %s <-mode L/T/LT> <-mdl model>" %sys.argv[0]) main(opt)
[評価結果表示]
1) tensorboard --logdir='./log/mnist'
2) ブラウザで, "http://localhost:6006"を開く
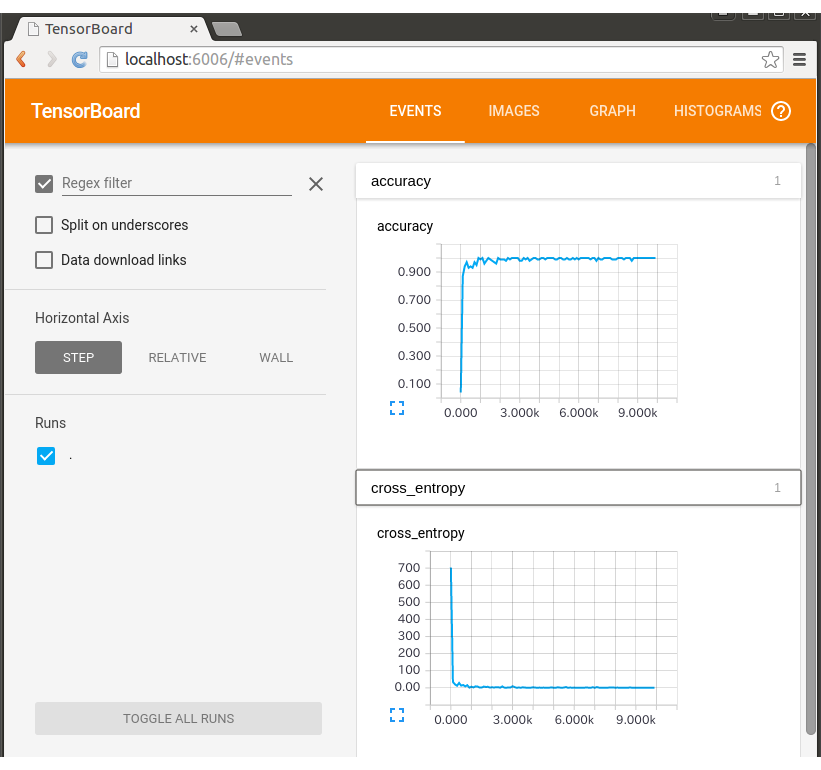
----
参照URL:
[1] TensorBoard: Visualizing Learning

|  データサイエンティスト養成読本 機械学習入門編 (Software Design plus)
| 
| 
|